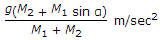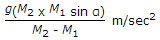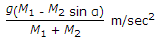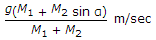C type of crushing machine.
ANS:C - both (a) & (b).
"Feed material" refers to the raw material that is fed into a processing or crushing machine for further treatment or size reduction. In various industries, the feed material can refer to different substances depending on the specific process or application. Here’s a general explanation:
Characteristics of Feed Material:
-
Physical Properties:
- Hardness: Indicates how resistant the material is to scratching or abrasion. For example, minerals like quartz are harder than materials like limestone.
- Brittleness: Refers to how easily a material breaks or fractures under stress. Brittle materials break into fragments without significant deformation.
- Density: Determines how tightly packed the molecules are within the material. High-density materials are heavier for their size.
- Particle Size Distribution: Refers to the range of sizes of particles within the material. It affects the efficiency of size reduction processes.
-
Chemical Composition:
- Composition of Minerals: Determines the behavior of the material under various conditions, such as heat or chemical reactions.
- Presence of Impurities: May affect the processing or performance of the material in industrial applications.
Importance in Industrial Processes:
-
Mining and Mineral Processing: Feed materials in mining operations include ores and minerals extracted from the earth. These materials are crushed, ground, and processed to extract valuable minerals.
-
Aggregate Production: In construction and road building, feed materials such as gravel, sand, and crushed stone are used to produce aggregates of various sizes.
-
Chemical Processing: Raw materials for chemical manufacturing include substances like chemicals, salts, and polymers that undergo chemical reactions or physical processing.
-
Food and Pharmaceutical Processing: In these industries, feed materials can include ingredients or raw materials used to manufacture food products, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
Processing Considerations:
-
Size Reduction: Crushing, grinding, and milling processes are used to reduce the size of feed materials to the desired particle size or distribution.
-
Mixing and Blending: Homogeneous mixing of feed materials is essential in various industrial processes to achieve uniform product quality.
-
Separation and Classification: Techniques such as screening and classification are used to separate feed materials into different size fractions or categories.
Conclusion:
Feed materials play a crucial role in industrial processes across various sectors, influencing the design and operation of processing equipment. Understanding the characteristics of feed materials is essential for optimizing process efficiency, product quality, and overall performance in industrial operations.
The "type of crushing machine" refers to the various equipment used in the process of reducing the size of feed materials through mechanical force. These machines are designed to break down larger particles into smaller ones, which may be required for further processing or for end-use applications in various industries. Here are some common types of crushing machines and their characteristics:
Types of Crushing Machines:
-
Jaw Crusher:
- Principle: Uses compressive force (pressure) to crush material between two jaws, one stationary and one movable.
- Application: Ideal for primary crushing of hard and abrasive materials like rock, gravel, and concrete.
- Advantages: Simple structure, reliable operation, and low operating costs.
-
Gyratory Crusher:
- Principle: Uses a mantle and a concave surface to crush large pieces of material by squeezing them between a stationary mantle and a rotating concave.
- Application: Suitable for primary crushing of large-sized materials like ores and rocks.
- Advantages: High capacity and efficient operation.
-
Cone Crusher:
- Principle: Uses a rotating mantle within a concave bowl to compress material against the walls of the bowl.
- Application: Used for secondary and tertiary crushing stages to produce finer and more uniform products.
- Advantages: Good control of product size, efficient operation with low operating costs.
-
Impact Crusher:
- Principle: Utilizes impact force to crush material. Material is fed into a chamber where a high-speed rotor impacts it against fixed anvils or curtains.
- Application: Effective for crushing medium-hard to hard materials such as limestone, dolomite, and gravel.
- Advantages: High reduction ratio, good particle shape, and versatility in applications.
-
Roll Crusher:
- Principle: Compresses material between two rotating rolls, either smooth or with teeth.
- Application: Used for secondary and tertiary crushing of friable and brittle materials like coal, salt, clay, and bauxite.
- Advantages: Low power consumption, adjustable product size, and compact design.
-
Hammer Mill:
- Principle: Uses high-speed rotating hammers to impact and shatter material against a stationary grate or screen.
- Application: Widely used for grinding and crushing materials to fine particles, such as grains, oilseeds, and biomass.
- Advantages: Versatility, ability to handle a wide range of materials, and relatively simple maintenance.
Selection Considerations:
-
Feed Material Characteristics: Each type of crusher is suited to different feed materials based on hardness, abrasiveness, and size distribution.
-
Product Requirements: Desired product size and shape influence the choice of crusher type and configuration.
-
Operating Conditions: Factors like throughput capacity, power requirements, and maintenance considerations impact the selection of crushing equipment.
Conclusion:
The type of crushing machine chosen for a specific application depends on factors such as the nature of the feed material, desired product specifications, and operational requirements. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of each type of crushing machine is crucial for selecting the most suitable equipment to achieve efficient and effective size reduction in industrial processes.
The constants (Kb, Kr, and Kk) used in the laws of crushing (Bond's law, Rittinger's law, and Kick's law) depend upon both (a) feed material and (b) type of crushing machine.
Here’s why:
-
Feed Material (a):
- The constants Kb, Kr, and Kk vary depending on the physical properties of the feed material, such as its hardness, brittleness, and compressive strength.
- Different feed materials require different amounts of energy for size reduction, influencing the value of these constants in the crushing laws.
-
Type of Crushing Machine (b):
- The type of crushing machine used (e.g., jaw crusher, cone crusher, impact crusher) affects how energy is applied to the feed material and the efficiency of the size reduction process.
- Each type of machine has its own characteristics that influence the crushing efficiency and therefore the value of the constants Kb, Kr, and Kk.
Therefore, the constants (Kb, Kr, and Kk) used in the laws of crushing depend on both the feed material and the type of crushing machine, making the correct answer both (a) & (b).
|