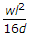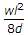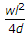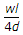ANS:C - both (a) & (b).
The horsepower required for a roll crusher is directly proportional to its capacity.
Here's an explanation:
-
Roll Crusher Basics:
- A roll crusher is a machine designed to reduce large rocks into smaller rocks, gravel, or rock dust. It consists of two large rolls, one of which rotates in opposite directions to crush the material fed into the crusher.
-
Horsepower Requirement:
- The horsepower (HP) required for a roll crusher primarily depends on its capacity, which refers to the maximum amount of material that the crusher can process per unit of time (typically measured in tons per hour).
- Higher capacity roll crushers require more horsepower to operate effectively because they handle larger volumes of material and require more power to crush and transport the material through the crushing chamber.
-
Reduction Ratio:
- The reduction ratio of a roll crusher refers to the ratio of the size of the feed material to the size of the crushed product after crushing.
- While reduction ratio affects the size of the final product, it does not directly determine the horsepower requirement of the crusher. Instead, it influences the operating conditions and efficiency of the crusher.
-
Conclusion:
- The horsepower required for a roll crusher is primarily determined by its capacity rather than its reduction ratio.
- Therefore, the correct answer is capacity. Horsepower is directly proportional to the capacity of the roll crusher, as higher capacities require more power to achieve efficient crushing operations.
Thus, the correct answer is
capacity.
The reduction ratio in the context of crushing equipment, such as crushers and grinding mills, refers to the ratio of the size of the feed material to the size of the crushed product. It quantifies the degree of size reduction achieved during the crushing or grinding process. Here’s a detailed explanation:
-
Definition:
- Reduction Ratio: It is defined as the ratio of the initial feed size to the final product size after crushing or grinding.
- Mathematically, it can be expressed as: Reduction Ratio=Feed SizeProduct Size\text{Reduction Ratio} = \frac{\text{Feed Size}}{\text{Product Size}}Reduction Ratio=Product SizeFeed Size where:
- Feed Size: The size of the material before crushing or grinding.
- Product Size: The size of the material after crushing or grinding.
-
Importance:
- The reduction ratio indicates how much the size of the feed material is reduced in relation to the final product size.
- It is a critical parameter in determining the efficiency of a crushing or grinding process because it affects the amount of energy required and the capacity of the equipment.
- Higher reduction ratios generally mean finer product sizes but may require higher energy consumption and more complex equipment.
-
Application:
- Crushers: In crushers, the reduction ratio can vary widely, depending on the type of crusher, the characteristics of the material being crushed, and the desired product size.
- For example, jaw crushers typically have a reduction ratio of 6:1 to 8:1, while cone crushers can achieve ratios of 10:1 to 25:1.
- Grinding Mills: In grinding mills, the reduction ratio typically ranges from 3:1 to 10:1 or more, depending on the type of mill and the material being ground.
-
Factors Influencing Reduction Ratio:
- Type of Crusher or Mill: Different types of crushers and mills have different inherent reduction ratios.
- Feed Material Properties: The hardness, moisture content, and size distribution of the feed material influence the achievable reduction ratio.
- Operating Conditions: The speed, setting, and operating parameters of the equipment affect the reduction ratio.
-
Effect on Product Quality:
- A higher reduction ratio generally results in finer product sizes, which may be desirable for certain applications such as fine grinding for mineral processing or producing smaller aggregate sizes in construction materials.
- However, excessively high reduction ratios can lead to excessive fines generation, increased energy consumption, and reduced throughput.
In summary, the reduction ratio is a key parameter in crushing and grinding operations that quantifies the size reduction achieved during the process. It is essential in optimizing the efficiency and performance of equipment in various industries, including mining, construction, and mineral processing.