- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 1
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 2
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 3
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 4
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 5
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 6
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 7
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 8
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 9
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 10
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 11
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 12
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 13
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 14
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 15
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 16
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 17
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 18
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 19
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 20
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 21
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 22
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 23
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 24
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 25
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 26
- Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Section 27


Networks Analysis and Synthesis - Engineering
Q1: A resistance R, inductance L and capacitance C are in series. The source frequency is adjusted to be equal to resonant frequency. The lower half power frequency is ω1. Another resistance R is added in series with the circuit. The new lower half power frequency will beA
ω1
B
less than ω1
C more than ω1
D
either more than ω1 or less then ω1
ANS:C - more than ω1 As R increases, Q decreases, bandwidth = |


For help Students Orientation
Mcqs Questions
One stop destination for examination, preparation, recruitment, and more. Specially designed online test to solve all your preparation worries. Go wherever you want to and practice whenever you want, using the online test platform.


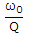 . Therefore, bandwidth increases. Hence lower half power frequency will be less than ωr.
. Therefore, bandwidth increases. Hence lower half power frequency will be less than ωr.