

Fluid Mechanics - Engineering
Q1: The equivalent diameter for pressure drop calculation for a fluid flowing through a rectangular cross-section channels having sides 'x' & 'y' is given byA 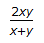
B 
C 
D 
ANS:A - The equivalent diameter (DeD_eDe) for pressure drop calculations in a fluid flowing through a rectangular cross-section channel with sides xxx and yyy can be determined using the hydraulic diameter concept. For a rectangular duct, the hydraulic diameter DhD_hDh is given by: Dh=4×AreaWetted perimeterD_h = \frac{4 \times \text{Area}}{\text{Wetted perimeter}}Dh=Wetted perimeter4×Area For a rectangular duct with sides xxx and yyy:
|


For help Students Orientation
Mcqs Questions
One stop destination for examination, preparation, recruitment, and more. Specially designed online test to solve all your preparation worries. Go wherever you want to and practice whenever you want, using the online test platform.

